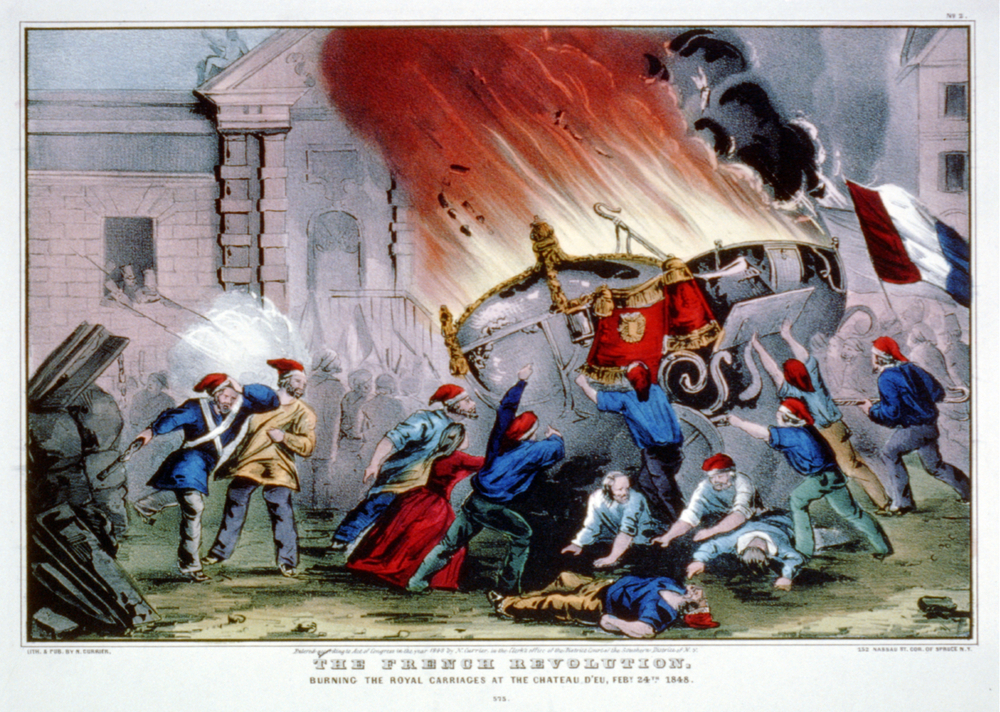
1. The French Revolution

-
1789 – 1799
It was started in 1789 and had a significant influence on both French and contemporary history, attempting to topple authoritarian monarchs and religions before establishing democratic and patriotic governance. Ultimately, it resulted in Louis XVI’s execution.
On July 14, 1789, rebels seized the Bastille, a medieval arsenal and jail, to equip themselves while also striking an emblem of the monarchy’s ultimate authority, according to historians. The next two months were called the Great Fear, as the country was immersed in violence and public panic.
It was a fight between the affluent and the poor, as French society at the time had a large difference between the upper and lower classes, with no middle class. Napoleon Bonaparte gained power in 1799, finally bringing the battle to a close. The French Revolution is remembered for overthrowing the French monarchy, which had reigned for generations; it displayed the people’s strength and capacity to really make a difference.